Simplifying NVMe over Fabrics with Centralized Discovery Controllers (CDC)

In the fast-paced world of data storage, NVMe® over Fabrics (NVMe-oF™) brings high performance to data centers, especially over IP-based networks. Central to this is the Centralized Discovery Controller (CDC), which automates and simplifies how NVMe hosts and subsystems interact.
This blog delves into the role of the CDC, how it enhances NVMe-oF environments, and the significant advantages it brings to data center scalability and efficiency.
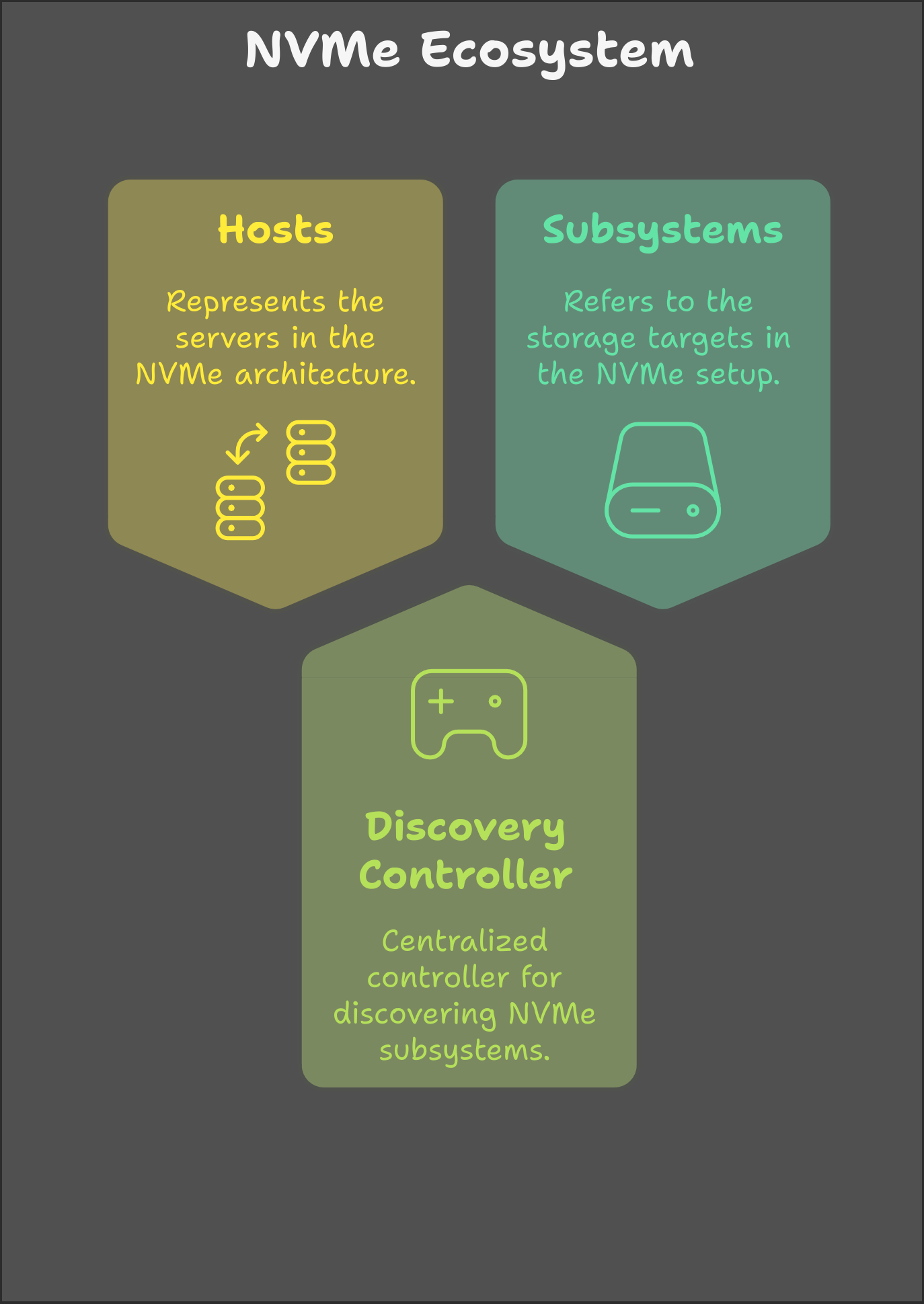
Understanding the Ecosystem: Hosts, Subsystems, and the CDC
Before exploring the CDC, it's essential to understand the key components:
- NVMe Hosts: Initiate commands to access storage.
- NVMe Subsystems (Targets): Provide storage volumes.
- Centralized Discovery Controller (CDC): Acts as an intermediary, managing connections between hosts and subsystems.
The Role of mDNS in Automatic Discovery
The Multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) is used for zero-configuration networking, enabling devices to discover each other without manual configuration. In the context of NVMe-oF:
- Registration with the CDC: Hosts and subsystems use mDNS to announce their presence, registering automatically with the CDC.
- Automatic Discovery: The CDC detects these announcements, simplifying network setup.
- Authentication and Verification: Ensures secure communication through the CDC.
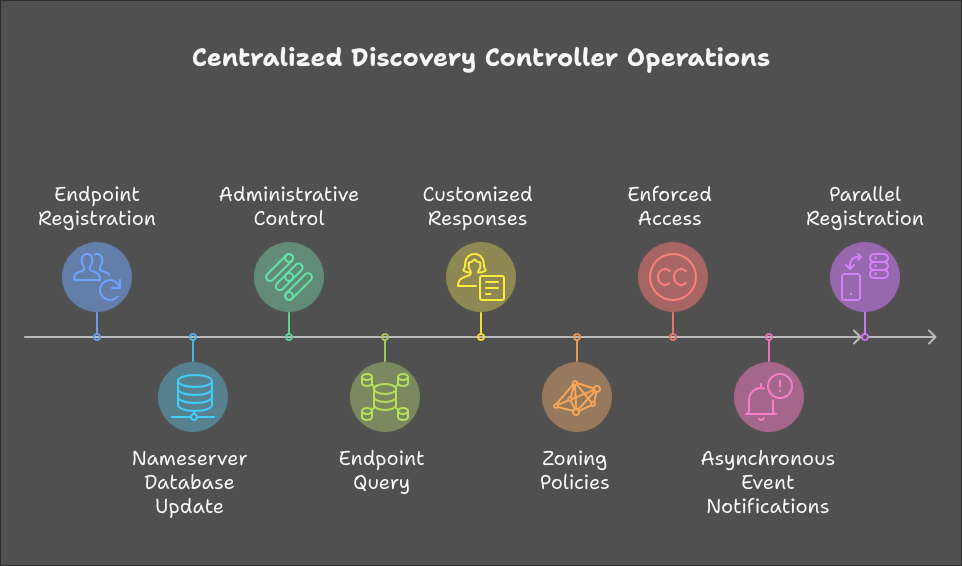
Centralized Discovery Controller (CDC): Key Services
The CDC serves as a central hub that streamlines discovery and management in an NVMe-oF environment. Its primary services include:
1. Endpoint Registration
- Automatic Registration: NVMe hosts and subsystems use mDNS to register with the CDC.
- Nameserver Database: The CDC maintains a Nameserver database with endpoint information.
- Administrative Control: Administrators can manage endpoints via the CDC web UI, including viewing, editing, or removing endpoints that are offline.
2. Endpoint Query
- Discovery Command: Hosts send a Get Log Page command to the CDC to obtain information about available subsystems.
- Customized Responses: The CDC provides each host with a tailored list of Allowed Subsystems based on zoning policies.
3. Zoning for Access Control
- Zoning Policies: Administrators define active zone groups to control which hosts can access specific subsystems.
- Enforced Access: The CDC ensures hosts only receive information about subsystems they are authorized to access.
4. Asynchronous Event Notifications (AEN)
- Real-Time Updates: The CDC sends AENs to hosts to notify them of changes, such as addition or removal of subsystems or updates in zoning policies.
- Dynamic Environment: Hosts receive immediate alerts, allowing them to adjust connections promptly.
5. Parallel Registration with NVMe Discover Commands
- Host Registration: Hosts use the NVMe Discover Registration command to register with the CDC.
- Parallel Operations: Multiple hosts can register simultaneously, improving efficiency during large-scale deployments.
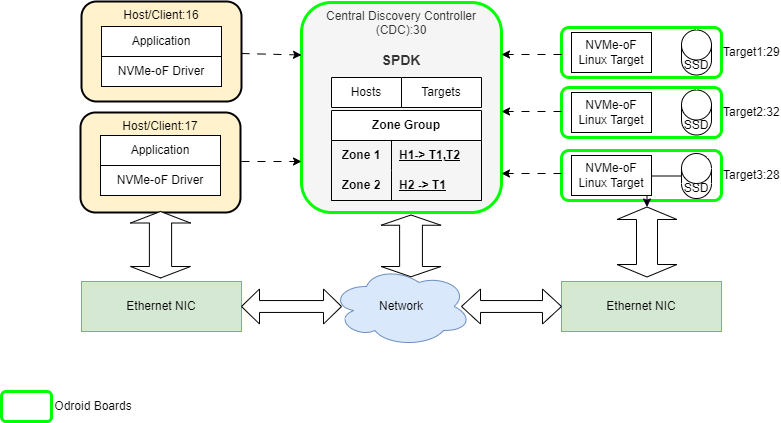
How the CDC Enhances NVMe-oF Networks
By centralizing discovery and management, the CDC offers several benefits:
- Simplified Management: Reduces manual configuration.
- Automated Discovery: Streamlines endpoint registration.
- Enhanced Security: Implements access control via zoning.
- Improved Scalability: Manages growth with less administrative effort.
- Dynamic Updates: Provides real-time network change notifications.
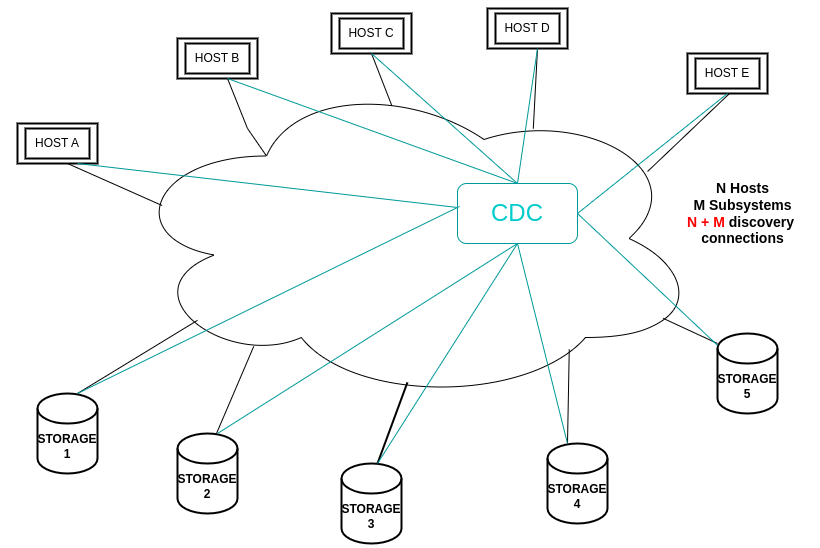
Comparing CDC with Direct Discovery
Before the CDC, hosts used Direct Discovery to connect with subsystems, where each host manually discovered and connected to each subsystem without an intermediary.
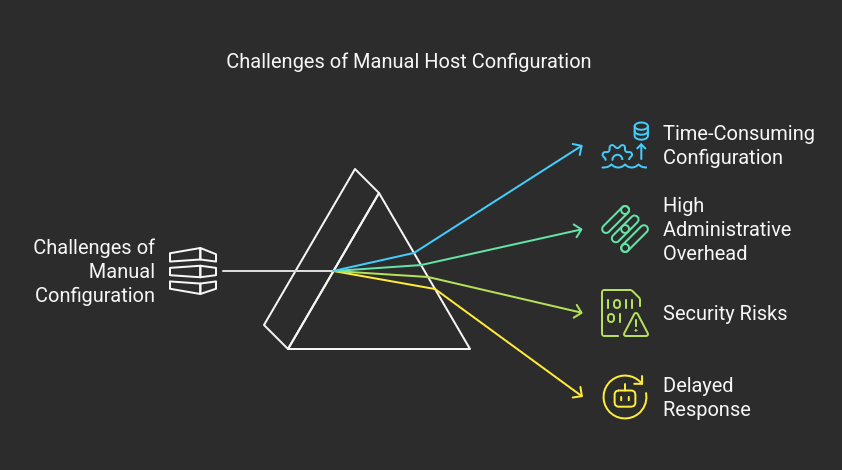
Limitations of Direct Discovery
- Manual Configuration: Hosts had to be individually configured to connect to subsystems.
- Management Complexity: No central point for policy enforcement or discovery information aggregation.
- Scalability Challenges: Increased number of hosts and subsystems led to significant management overhead.
- Delayed Updates: Hosts were not promptly informed of changes in the network.
Advantages of CDC Over Direct Discovery
|
Feature |
Centralized Discovery Controller (CDC) |
Direct Discovery |
|
Discovery Method |
Automated via mDNS and CDC |
Manual configuration by the host |
|
Management |
Centralized control through CDC |
Decentralized, managed individually |
|
Scalability |
Highly scalable with reduced overhead |
Limited scalability due to complexity |
|
Security |
Enhanced through zoning policies |
Less efficient, harder to enforce |
|
Network Updates |
Real-time AENs keep hosts updated |
Hosts unaware of changes without manual checks |
Real-World Application: CDC in Large-Scale Data Centers
Consider a data center with:
- 5,000 NVMe Hosts
- 1,000 NVMe Subsystems
- Petabytes of Data
Challenges Without CDC
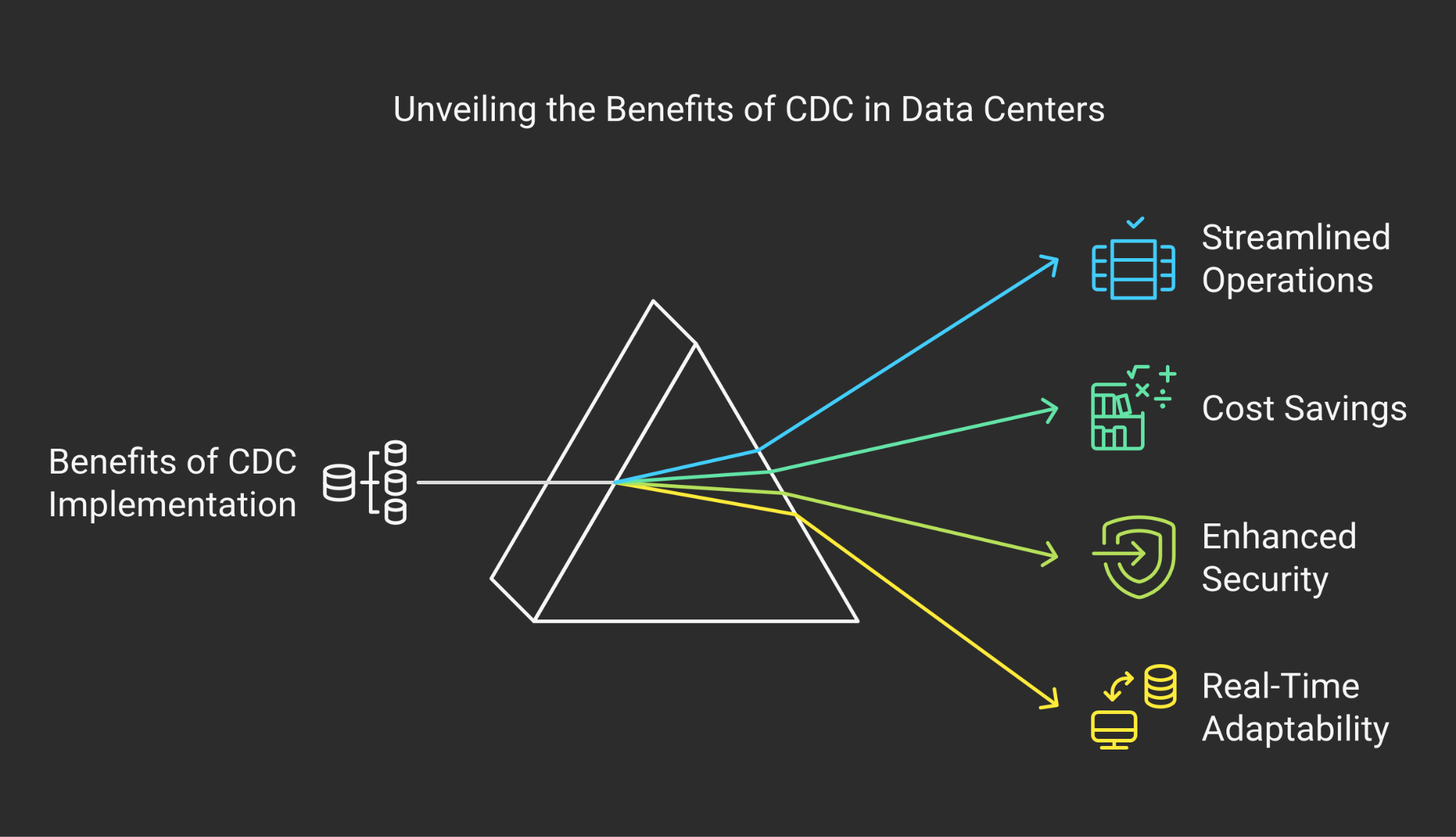
Benefits of Implementing CDC
Conclusion: Embracing CDC for a Future-Ready Infrastructure
The Centralized Discovery Controller revolutionizes NVMe-oF by automating discovery, managing access through zoning, offering real-time updates, and enabling parallel host registration, thus tackling key data center challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Efficiency: Reduces management overhead through automation.
- Scalability: Allows easy expansion without complexity.
- Security: Improves access control with zoning and authentication.
- Adaptability: Ensures the network remains responsive with real-time notifications.
- Simplified Deployment: Makes host onboarding smoother with parallel registration.
Is your data center ready to leverage the benefits of a Centralized Discovery Controller? Implementing a CDC in your NVMe-oF architecture could be the strategic move that elevates your infrastructure's efficiency and scalability.
Contributors
Principal Engineer | ASIC Design Verification | Storage and Silicon Enthusiast
Prajakta Rohom is an experienced Principal Engineer working with Aaroh Labs for the last 4 years with a knack for tackling complex silicon challenges. Prajakta has a track record of 18+ years in semiconductor design verification and a current focus on storage solutions.
Engineer-1 | Storage Systems Developer
Aman Sharma is an Engineer at Aaroh Labs with 2+ years of experience, driving advancements in storage


